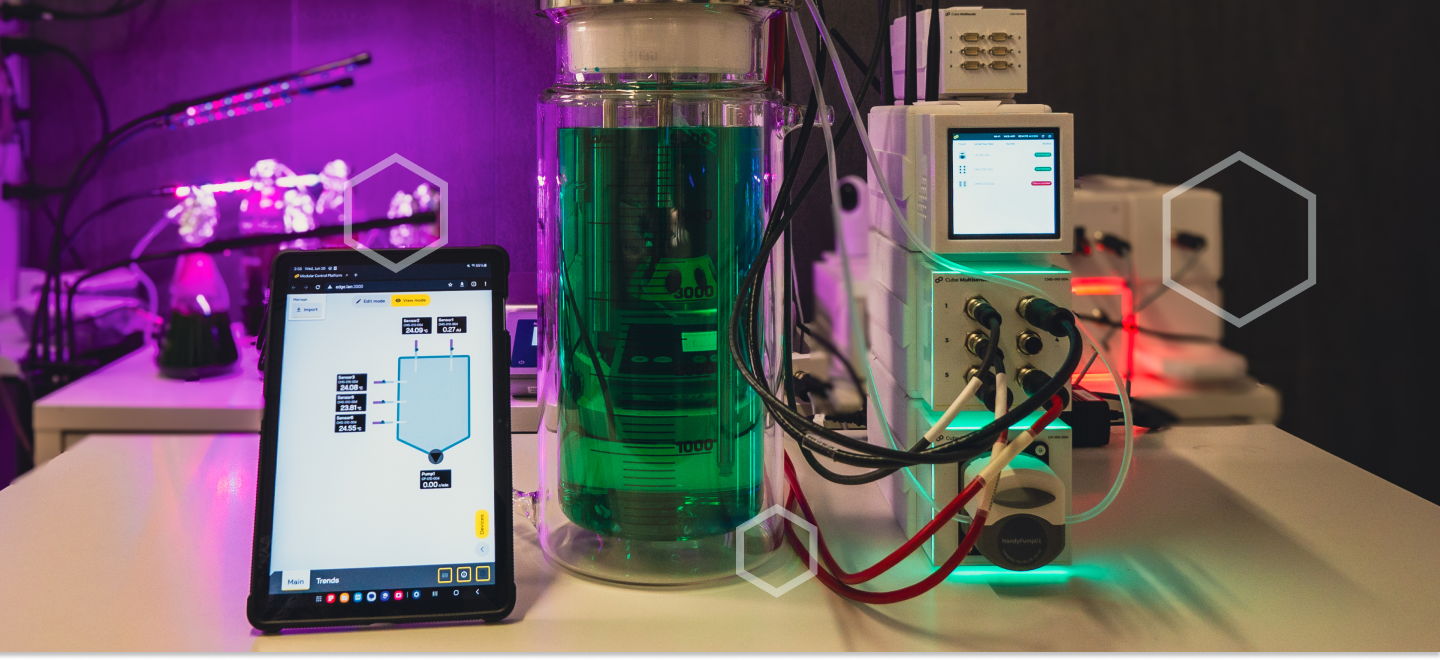

Benchtop Bioreactor Solutions for Efficient Data Integration
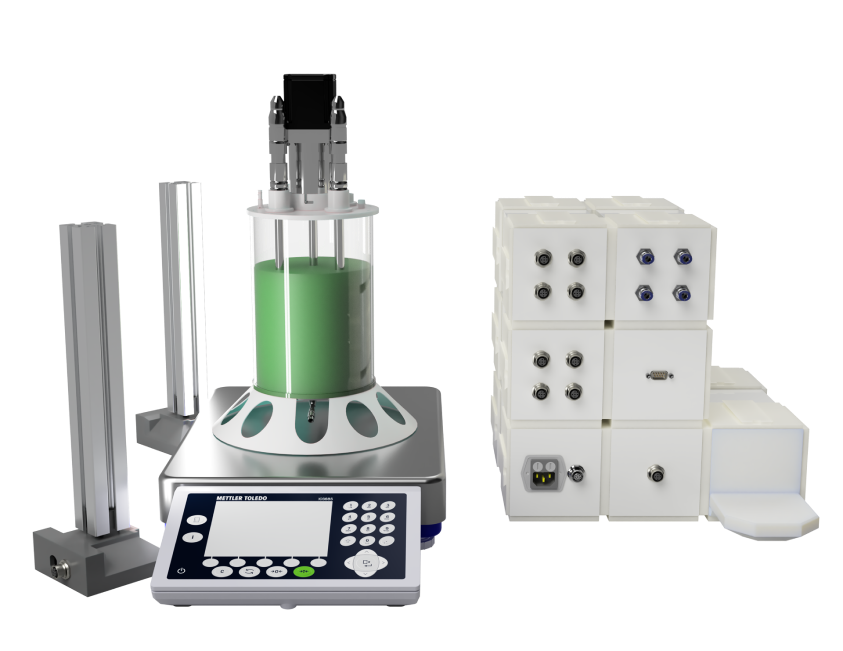

Handy. Smart. Flexible.
Our bench-top modular bioreactor is ideal for daily work and offers unparalleled high quality. It enables data-driven decision-making, sets new standards in control and automation, prioritizes user-centric safety, and features an ergonomic design.
Ideal for a wide variety of applications, from fermentation to cell culture.
01
CHALLENGE
How can I automate my work and spend more time on science?
You can now automate your workflow during routine tasks using Cubes and a data collection and visualization platform (Control Platform). These incredible tools allow you to monitor and control processes in real-time and make data-driven decisions faster, freeing up more time for scientific analysis.
How can I get easy access to the data from my bioprocess?
It's so straightforward! All you have to do is open the Control Platform, which allows you to view, download, and manage process data effortlessly.
How can I use advanced analytics, ML and AI in my lab?
You can use advanced analytics, ML, and AI in your lab by using our tools to analyze large datasets for trends, optimize experimental conditions, automate routine analysis, and predict outcomes, ultimately increasing your research's accuracy, efficiency, and innovation.
How can I save lab workspace?
Our Cubes are the perfect solution for your lab! They're small, easy to configure, and can be built into any shape you can imagine. They're flexible enough to fit into any layout and free up workspace, which is very important in labs.
02
SOLUTIONS
- Cell cultivation in bioreactor
- Microalgae cultivation
- Production of monoclonal antibodies
- Fermentation
- Production of antibiotics
03
CUBE BIOREACTOR SETUP
Join till 28th of
Feb and get
a special
discounted offer
for Lab Innovators!
Cube Multisensor
Allows for the simultaneous collection of real-time data from six different sensors via the Modbus RS485 communication protocol. This enables the monitoring of a wide range of parameters, with the flexibility to select the specific parameters of interest (e.g., pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, foam, CO2, redox).
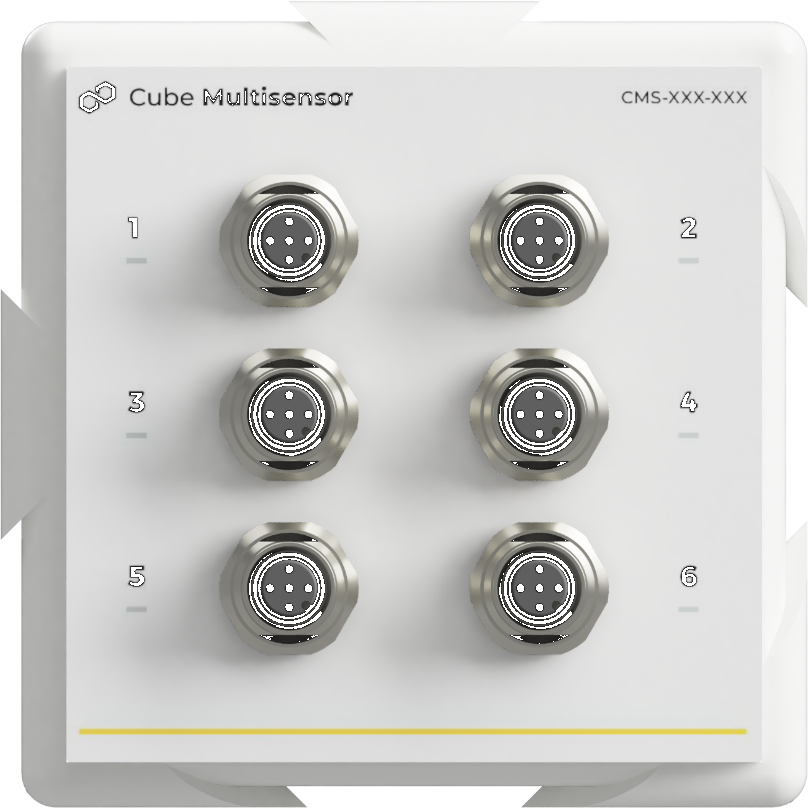

- Up to 6 digital sensors
- Compatible with Hamilton and Mettler Toledo probes by default
- Zero config, plug & play
- Works with Cube Edge out of the box
- One cable for power & data
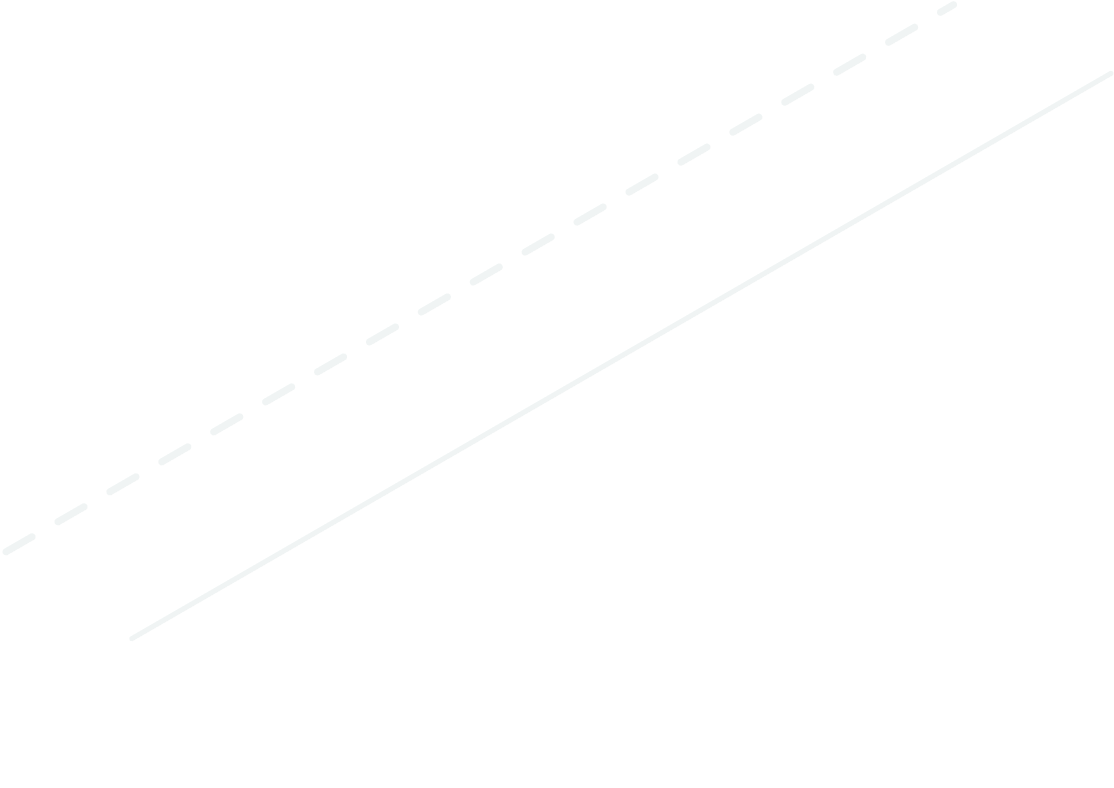
Cube Multiscale
Enables the simultaneous, real-time collection of data from six different scales over Modbus RS232. This allows for integrating scales with varying operating ranges, enabling them to be adapted as required.
- Up to 6 industrial scales
- Compatible with Mettler Toledo scales by default*
- Zero config, plug & play
- One cable for power & data
Cube Pump
A peristaltic pump offers complete control over the direction and speed of fluid flow. This makes it ideal for dosing various substances into the bioreactor, including antifoam agents, acids, bases, and media.

- Flow: 0.0033 - 365.69mL/min
- Speed: 0.1 - 300rpm
- Compatible with tubes from 0.8x1.6 to 3.1x1.6 mm
- Zero config, plug & play
- One cable for power & data
Cube Led Controller
The integrated LED panels and controller enable precise lighting control, ensuring optimal illumination in critical process settings.

- Up to 2 independent LED Modules
- Color temperature 4000K
- Luminous flux: min. 55 μmol/s max. 900 PPFD Min. 2800 lx max. 40 000 lx
- Measured at a distance of 1 cm from the light source
- Zero config, plug & play
- One cable for power & data
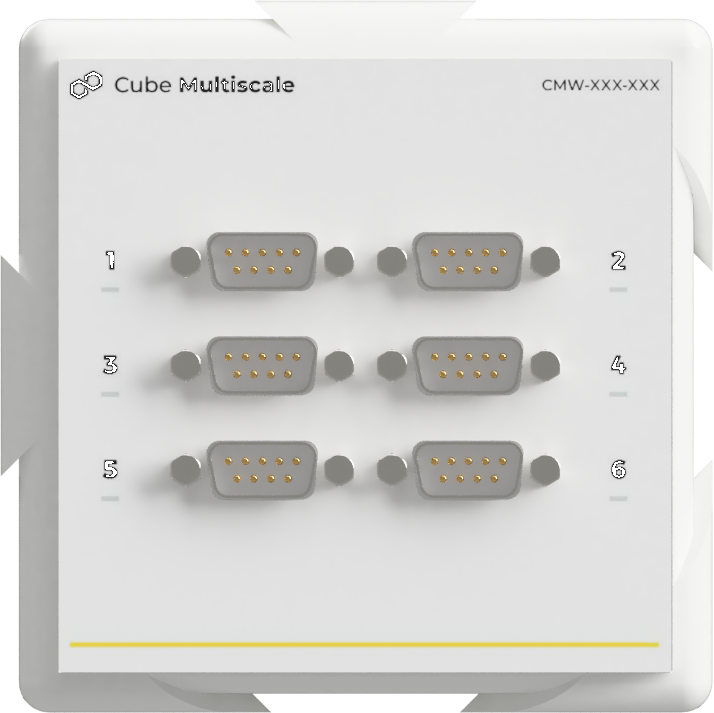
Cube Sparger
The integrated controller offers straightforward and effective control of the gas flow, with the ability to manage up to three distinct gas lines.
- Stirrer capabilities*:
- Up to 3 independent channels
- From 100SCCM to 100SLPM
- 9 gases: air, N2, O2, CH4, He, H2, Ar, CO2, N2O
- Operating pressure up to 145 PSIA
- Zero config, plug & play
- One cable for power & data
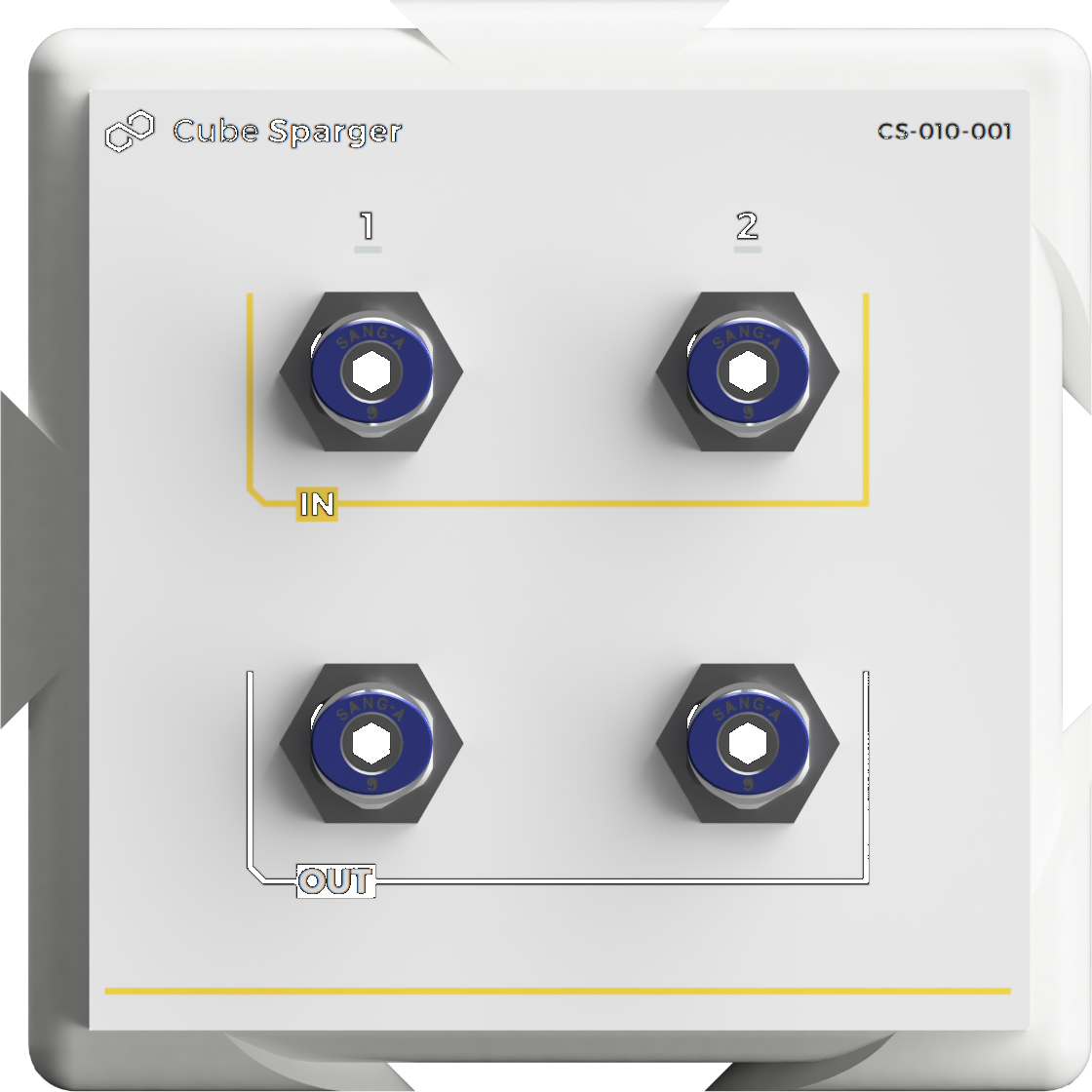
Cube Agitator
Cube able to control a mechanical stirrer to stir or mix fluids in a tank or container to ensure uniform consistency and prevent sedimentation. The mechanical stirrer can be equipped with different blades or impellers, depending on the specific mixing requirements, and they operate by creating a flow within the liquid, enhancing the reaction, and improving heat transfer and mass transfer within the mixture.
- Speed range [1/min]: 40 – 2000 rpm
- Stirring quantity, max. (H2O) [l]: 200
- Digital display type: LCD
- Torque, max. [Ncm]: 150
- Timer display: Yes
- Timer function: Yes
- Torque display: Yes
Cube Edge
Main unit, provides power and data connection to all connected devices. This Cube is a fundamental component of the system - the other Cubes can be configured according to the user's requirements.
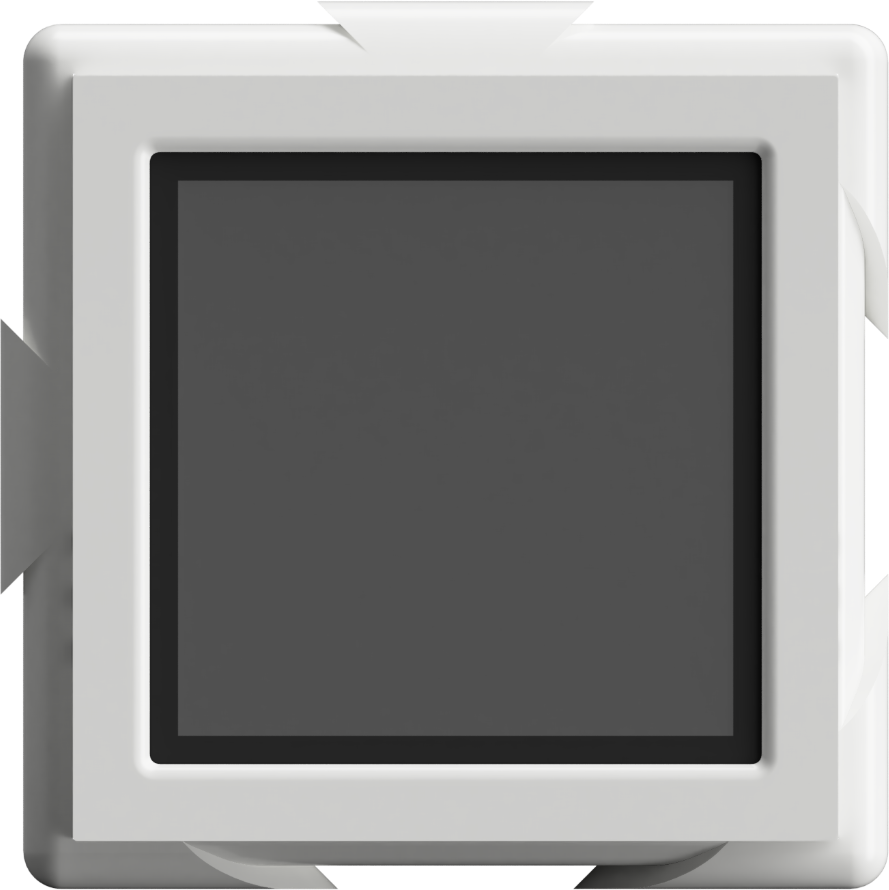
- Touchscreen with basic info about other Cubes to display device parameters
- Operate with as many Cubes as it's needed
- Wireless connection with end-user devices
- Remote support through network access
- Modular Control Platform App with Lab-oriented capabilities
Capture the power of modularity
04
DIGITAL FUNCTIONS
Data integration
All sensors are connected to a single software platform for data visualization.
Remote Monitoring & Process Control
Live online view of culture parameters with the ability to change them.
Plug & Play exchangable components
Easily replace faulty components without stopping the bioprocess or servicing the bioreactor.
Modular equipment
Quickly adapt bioreactor components to cultivation needs as easy as building blocks.
Scalability
Quickly adapt bioreactor components to cultivation needs as easy as building blocks.
Data Collection and Visualization
All data is collected in one place for easy access, analysis, and sharing
User-friendly interface
Well-designed application interface enhances user experience and speeds up the training process.
05
DEVICE FUNCTIONS
- pH
- Temperature
- DO
- Cell Density
- CO2
- Fluid pumping
- LED lighting
- Aeration
- Flow measurements
- Temperature control
Monitoring environmental parameters (e.g. temperature, humidity)
06
BENEFITS
-
Reducing the need for extensive training and minimizing human errors.
-
Minimizing downtime and maximizing the utility of the lab devices
-
Gaining access to data driven process decisions
-
Automating bioprocesses in high efficient and cost-effective way
-
Easy and rapid assembly and operation
07
USE CASES
The proposed set of equipment for these types of processes consists of modules to provide:
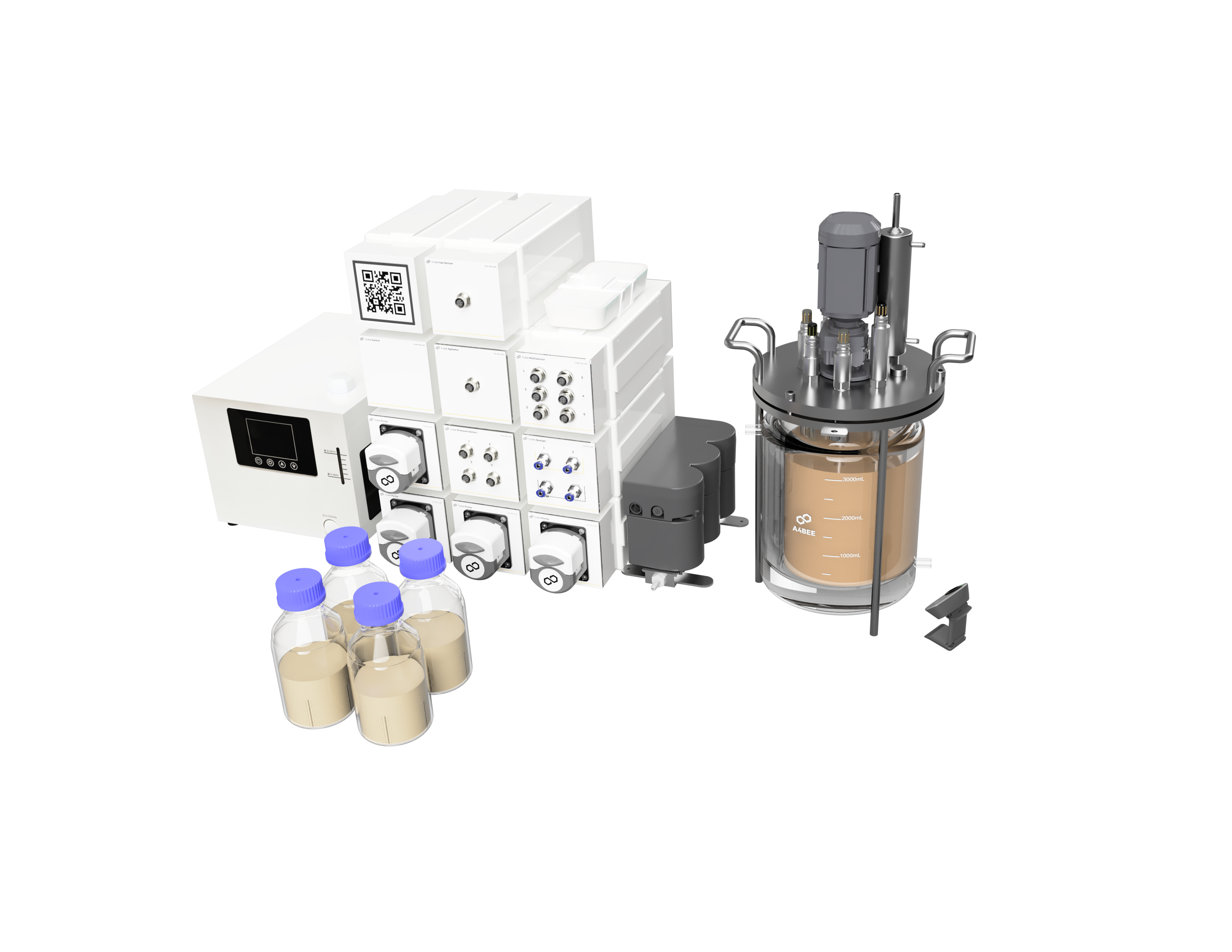

Microbial fermentation
| Cube Sparger | Gas supply |
| Cube Multisensor | Monitoring of parameters via probes: pH, temperature, O2, DO, foam sensor |
| Cube Agitator | Stirring |
| Cube Temperature Controller & Chiller |
Temperature control |
| Cube Pump | Liquid supply and sampling |
| Cube Gas Sensor | Exhaust gas monitoring |
| Exhaust Cooler | Gas condensation |
| Cube Pressure Sensor | Outlet pressure monitoring |
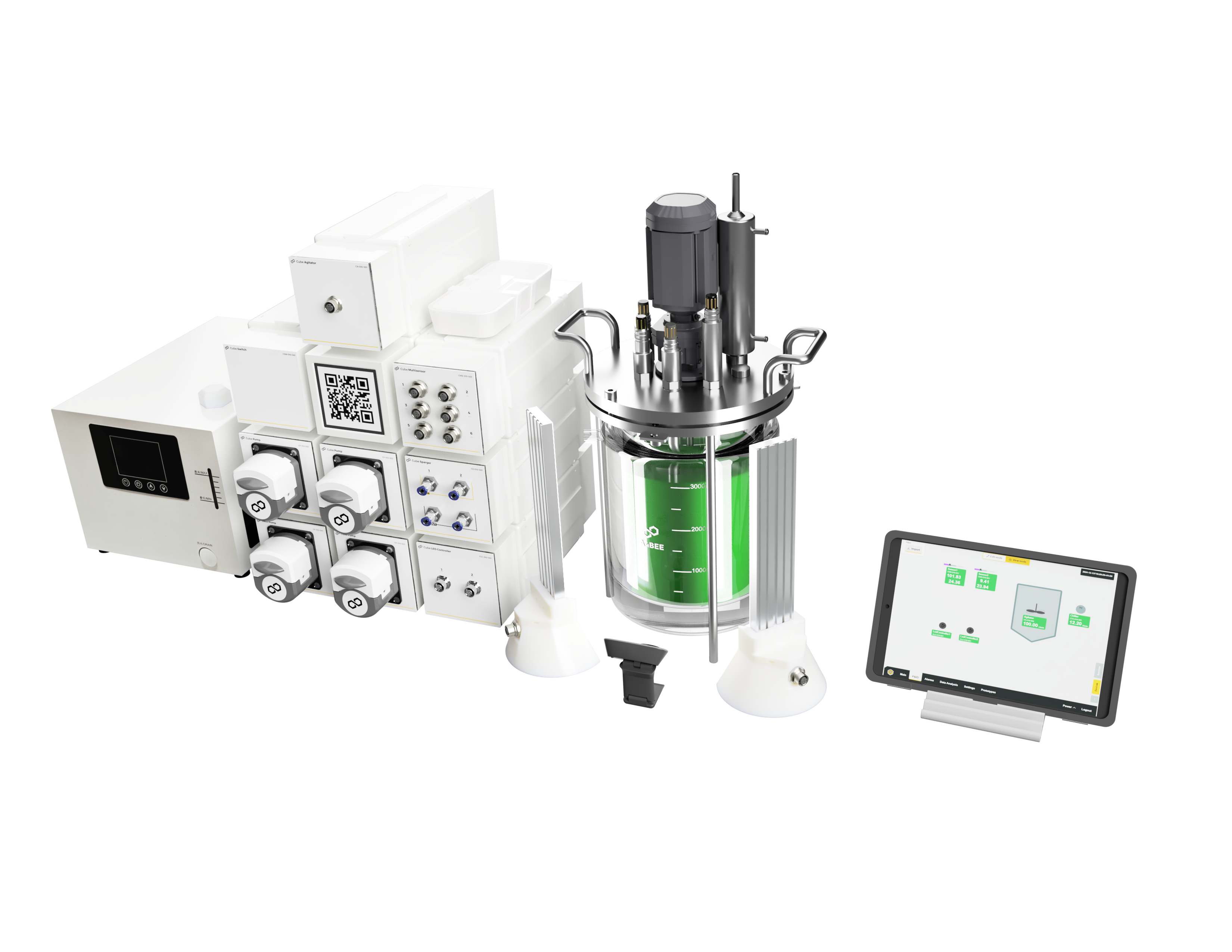

Microalgae Culture
| Cube Sparger | Gas supply |
| Cube Multisensor& set of probes | Monitoring of parameters via probes: pH, temperature, O2, DO, foam sensor |
| Cube Agitator | Stirring |
| Cube Temperature Controller & Chiller |
Temperature control |
| Cube LED Controller& LED Panels | Lighting |
| Cube Pump | Liquid supply and sampling |
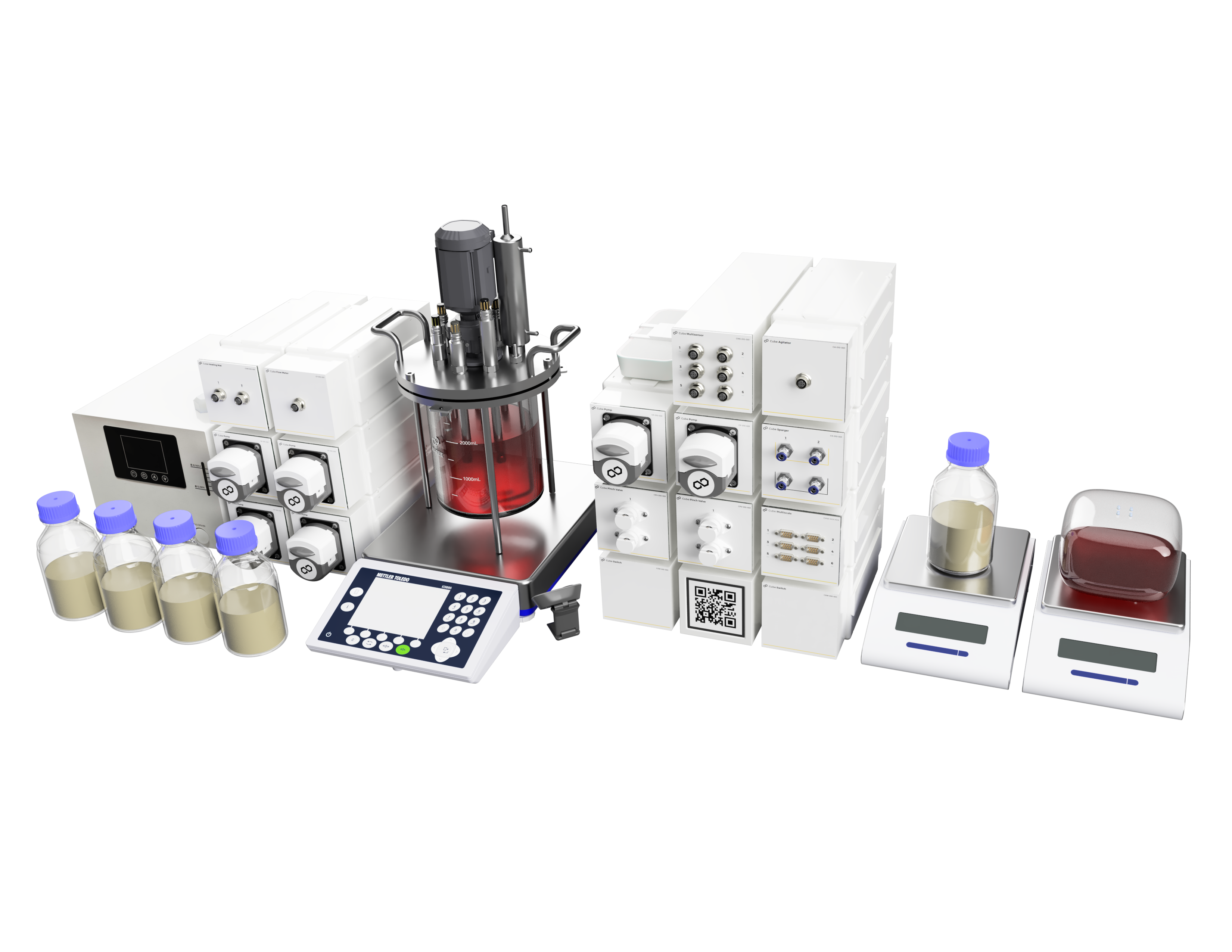

Cell cultures (i.e. CHO)
| Cube Sparger | Gas supply |
| Cube Multisensor& set of probes | Monitoring of parameters via probes: pH, temperature, O2, DO, foam sensor |
| Cube Agitator | Stirring |
| Cube Temperature Controller & Chiller |
Temperature control |
| Cube Pump | Liquid supply and sampling |
| Cube Pinch Valve | Valve control |
08
FAQ
What is bioprocessing?
What is bioreactor fermentation?
What is cell culture?
What is cell culture media?
What is a bioreactor?
Bioreactor vs Photobioreactor - what's the difference?
What are the challenges of bioreactor-driven processes?
- - Contamination and infection are among the biggest challenges when conducting bioreactor processes. Maintaining internal sterility during all stages of bioproduction is extremely important and affects the final product and bioproduction efficiency.
- - Human error - errors in media preparation, bioreactor handling, or sampling can result in contamination or inappropriate culture conditions.
- - Optimization of conditions and scalability - when scaling up to larger bioreactors, culture conditions such as mixing, aeration, and media composition need to be adjusted.
- - Monitoring and control of bioprocesses. The complexity and sensitivity of biological systems, high sterility requirements, and difficulties with real-time measurements all make it necessary to have advanced technology and expertise to maintain optimal production conditions.
How do I choose the right bioreactor?
- - What kind of microorganism you're working with (yeast, bacteria, algae, cell lines)
- - What the microorganism needs (e.g., phototrophic organisms will require a light source)
- - Scale (lab scale, pilot scale, industrial scale)
- - How you want to culture the microorganism (batch, feed-batch, continuous)
- - The type of bioreactor
- - A monitoring and control system
- - Which material do you prefer for constructing the reactor (such as steel, glass, or single-use plastic)
